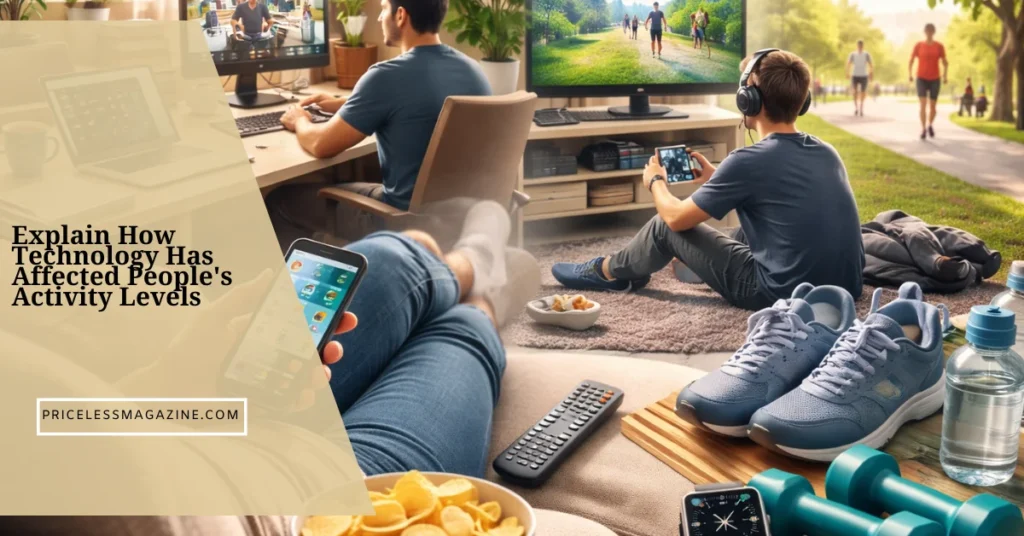
Technology has significantly reduced people’s activity levels by replacing physical movement with screen based convenience in work, education, transport, and entertainment. While technology has improved efficiency and comfort, it has also increased sedentary behavior, reduced daily movement, and changed how often people exercise.
To explain how technology has affected people’s activity levels clearly, it is important to understand how everyday routines have shifted, how physical activity has declined, and how modern lifestyles now rely more on sitting than moving.
What Activity Levels Mean In Everyday Life
Activity levels refer to how much physical movement a person performs throughout the day. This includes walking, standing, lifting, exercising, and even small movements that naturally occur during daily tasks.
An active lifestyle involves frequent movement across work, home, and leisure time. A sedentary lifestyle involves long periods of sitting with minimal physical effort. Activity levels matter because the human body is designed for movement, not prolonged stillness.
When activity levels drop for extended periods, the body gradually adapts in ways that reduce strength, energy, and overall health.
How Daily Life Changed With The Rise Of Technology
Technology has reshaped daily routines by reducing the need for physical effort. Tasks that once required movement are now completed with minimal motion through digital tools and automation.
Work environments shifted from physically demanding roles to desk based jobs. Education moved from classrooms to screens. Leisure activities transitioned from outdoor play to digital entertainment.
Over time, these changes removed natural movement from everyday life.
Technology And The Increase In Sedentary Behavior
Sedentary behavior has increased alongside widespread technology use. Many people now spend several hours sitting while working on computers, using smartphones, watching television, or gaming.
Screen time often replaces activities that previously required movement. Long sitting periods reduce muscle engagement and slow calorie use, even when screen based tasks feel productive.
This rise in sedentary behavior is one of the clearest ways to explain how technology has affected people’s activity levels.
The Role Of Digital Devices In Reduced Physical Movement
Smartphones, tablets, and computers are central to modern life, but they encourage stillness. These devices provide constant access to communication, entertainment, and information without requiring movement.
Streaming platforms promote long viewing sessions. Social media keeps users engaged for extended periods. Mobile apps reduce the need to walk, shop, or interact physically.
The result is less spontaneous movement and fewer opportunities for physical activity.
How Technology Has Reduced Exercise In Daily Routines
Technology has reduced both structured exercise and unstructured movement. Many people now drive short distances instead of walking, use elevators instead of stairs, and order food instead of shopping in person.
Incidental exercise that once occurred naturally has declined. Daily step counts are lower, and physical effort is no longer built into routines.
Even when people plan workouts, long sitting periods outside exercise still lower overall activity levels.
Physical Health Effects Of Lower Activity Levels
Lower activity levels have clear physical consequences. Reduced movement contributes to weight gain, loss of muscle strength, and decreased cardiovascular endurance.
Inactive lifestyles are linked to obesity, joint stiffness, poor posture, and slower metabolism. Over time, reduced activity also affects bone density and flexibility.
These outcomes show how technology influences health indirectly by limiting movement.
Mental And Emotional Effects Of Reduced Activity
Physical activity supports mental well being by improving mood, focus, and energy. When movement decreases, mental health can also be affected.
Lower activity levels are associated with fatigue, reduced motivation, and increased stress. Physical inactivity limits the natural release of endorphins that help regulate emotions.
Technology itself is not harmful, but excessive passive use can replace movement that supports emotional balance.
Technology In Work And Education Environments
Modern work and education rely heavily on digital platforms. Remote work, online meetings, and virtual learning reduce the need to move between locations.
Students spend more time seated during screen based lessons. Workers remain at desks for long hours with minimal physical breaks.
While technology improves access and efficiency, it also removes built in movement from daily schedules.
Passive Versus Active Technology Use
Not all technology affects activity levels in the same way. Passive technology use involves sitting and consuming content with little physical engagement.
Active technology use encourages movement, such as fitness tracking, exercise apps, and movement based gaming.
The impact on activity levels depends more on usage habits than on technology itself.
Positive Ways Technology Can Increase Activity Levels
Technology can support physical activity when used intentionally. Fitness apps, wearable trackers, and online workouts encourage movement and accountability.
Step counters motivate walking. Guided workouts provide structure. Activity reminders prompt breaks from sitting.
When used correctly, technology can reduce inactivity rather than increase it.
Differences In Activity Impact Across Age Groups
Children And Adolescents
Children spend more time on screens than previous generations. Outdoor play has declined, and digital entertainment often replaces physical games.
This shift affects motor development, fitness habits, and long term activity patterns.
Adults And Working Professionals
Adults experience reduced movement due to desk jobs and screen based tasks. Time constraints and convenience further limit exercise.
Many adults meet work demands but struggle to maintain consistent physical activity.
Older Adults
Technology can reduce movement in older adults, but it can also support activity through guided programs and monitoring tools.
The impact depends on accessibility and usage patterns.
Transport Technology And Reduced Physical Effort
Modern transportation reduces walking and cycling. Cars, ride services, and delivery apps eliminate the need to move between locations.
Short trips that once involved walking now involve sitting, reducing daily movement over time.
Long Term Lifestyle Patterns Caused By Technology
Technology has shaped long term habits. Children grow up using screens, adults work through screens, and leisure revolves around screens.
These patterns normalize inactivity and reduce awareness of movement needs. Over time, low activity becomes the default rather than the exception.
Frequently Asked Questions
Find answers to the most common questions
How has technology changed physical activity in daily life?
Technology has replaced many physical tasks with digital alternatives, leading to more sitting and less natural movement.
Is technology the main cause of inactivity?
Technology is a major contributor, but lifestyle habits, work structures, and environment also play important roles.
Can technology help improve activity levels?
Yes, fitness apps, trackers, and guided workouts can increase movement when used intentionally.
Why do people sit more because of technology?
Digital tools allow work, communication, and entertainment to happen without physical effort, encouraging prolonged sitting.
How can people stay active while using technology?
Setting movement reminders, limiting passive screen time, and using active technology tools help maintain healthy activity levels.
Conclusion
To explain how technology has affected people’s activity levels, it is clear that modern tools have reduced movement while increasing convenience. Daily routines now involve more sitting, less incidental exercise, and greater reliance on screens.
At the same time, technology offers tools that can support movement when used intentionally. The challenge is not technology itself, but how it is integrated into daily life. Awareness, balance, and conscious choices determine whether technology limits or supports physical activity.